Know Solar
Renewable Solar Energy
Energy can be obtained from natural, virtually inexhaustible sources that replenish naturally. Termed renewable energy, is also known as clean energy or green energy.
Solar, wind, biomass, geothermal, hydropower, ocean energy, and bioenergy are various types of renewable energy sources.
Any form of energy produced by the sun is called solar energy. This energy harnessed from the sun is converted into usable solar energy. The technologies that convert this energy are called solar energy systems.
These technologies are divided into two categories:
- Solar Photovoltaics (PV): Considered the fastest-growing renewable energy technology, photovoltaic devices transform sunlight into DC (Direct Current) electricity.
- Solar Thermal: This technology uses the sun’s heat energy for heating or producing electricity.
Sustainable solutions for energy consumption have increased globally to protect the environment and positively impact the planet.
Be a part of the change and switch to solar today!

How Does Solar Work?
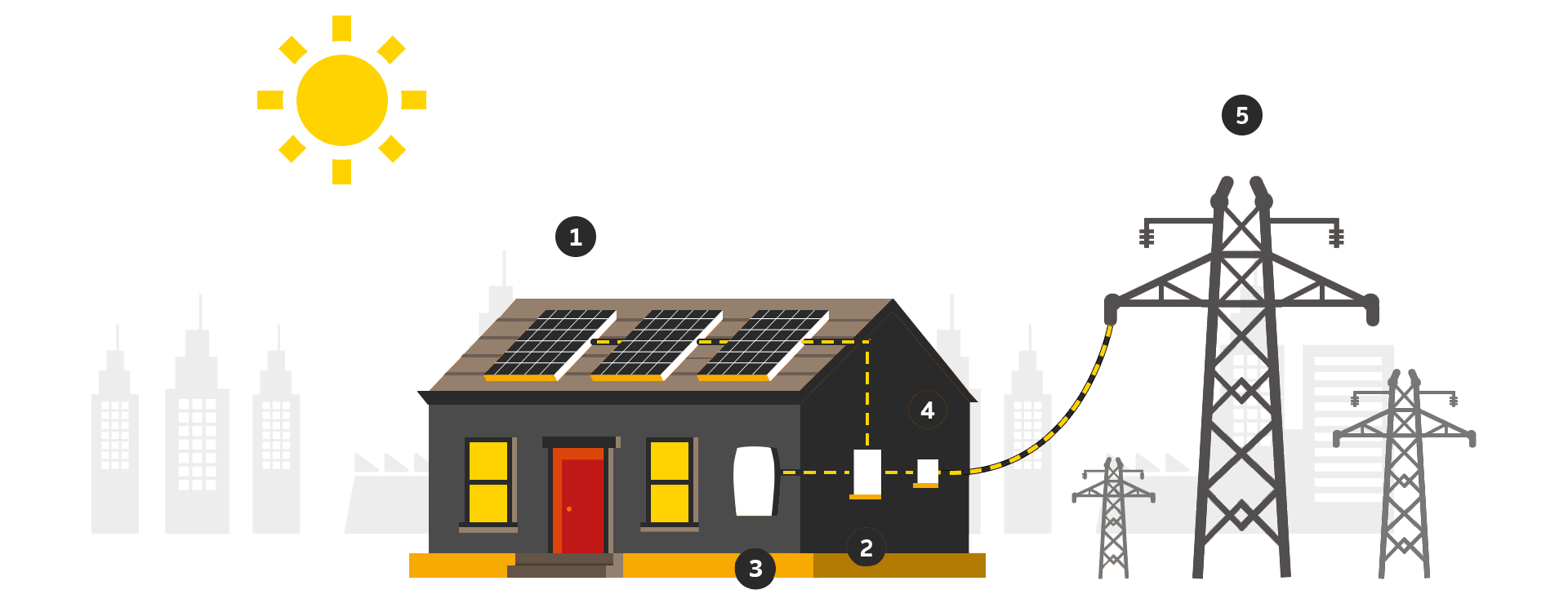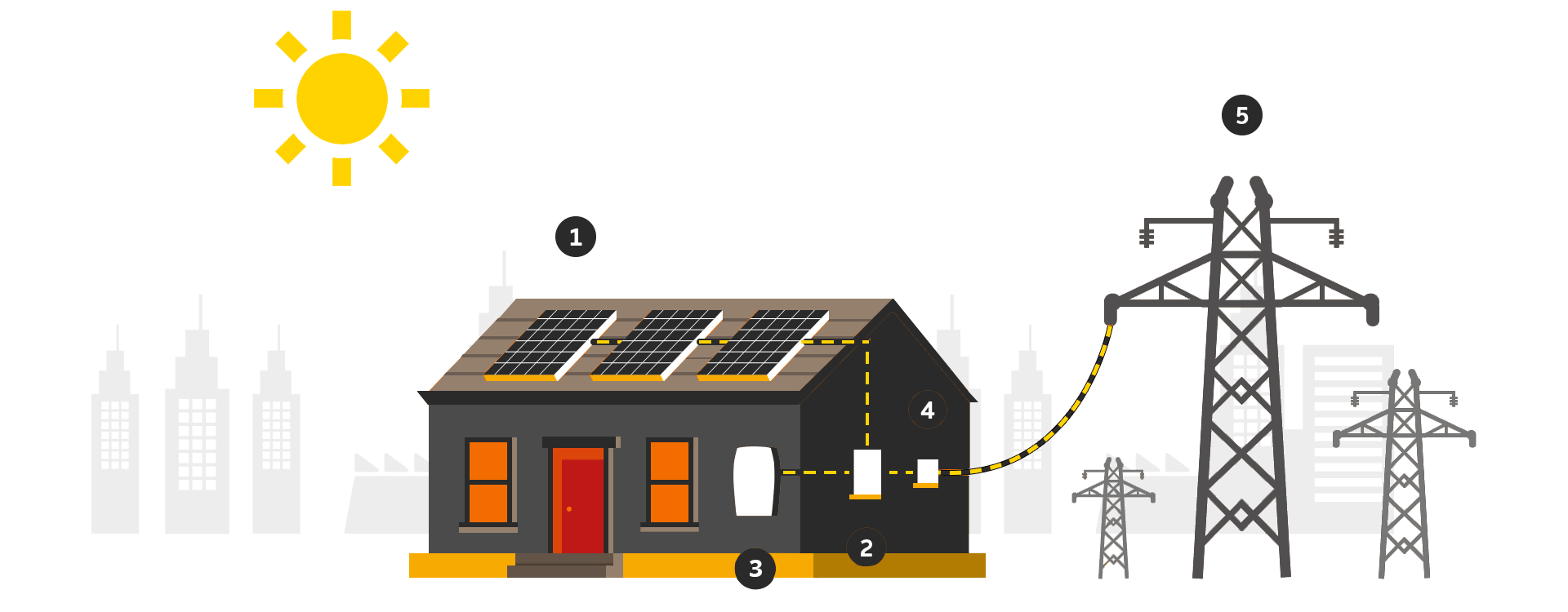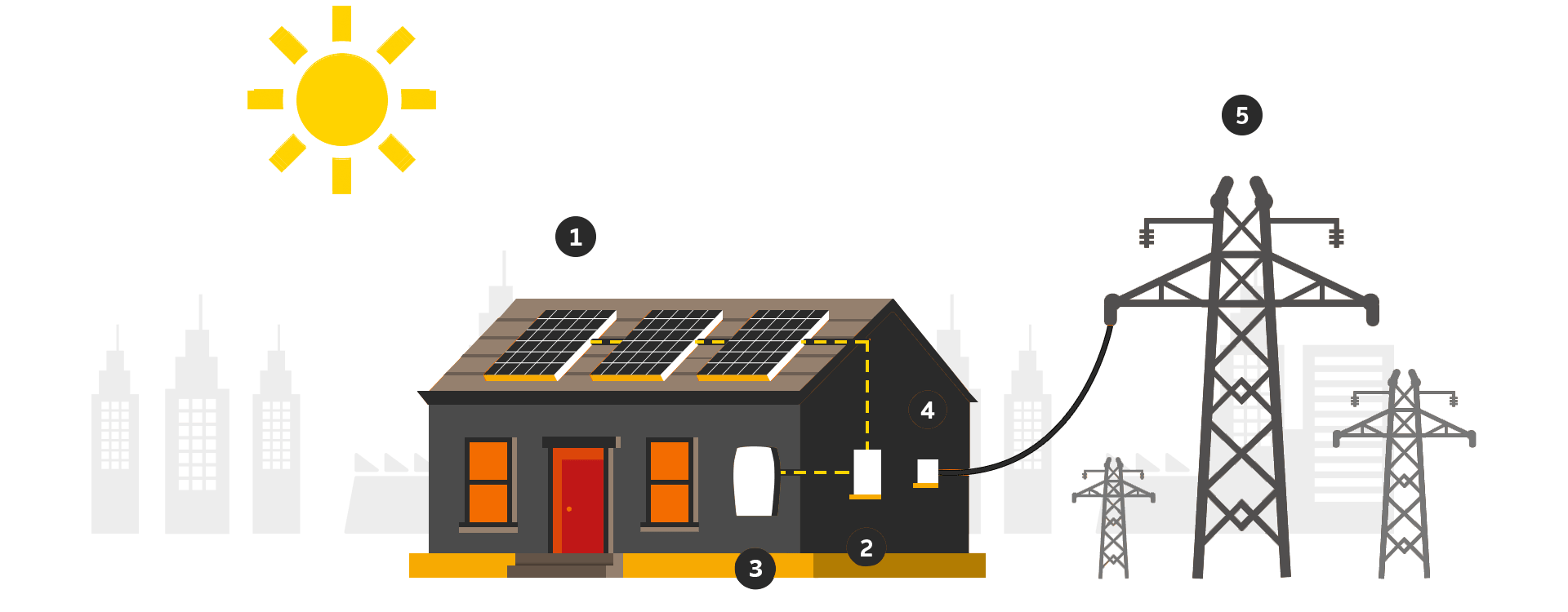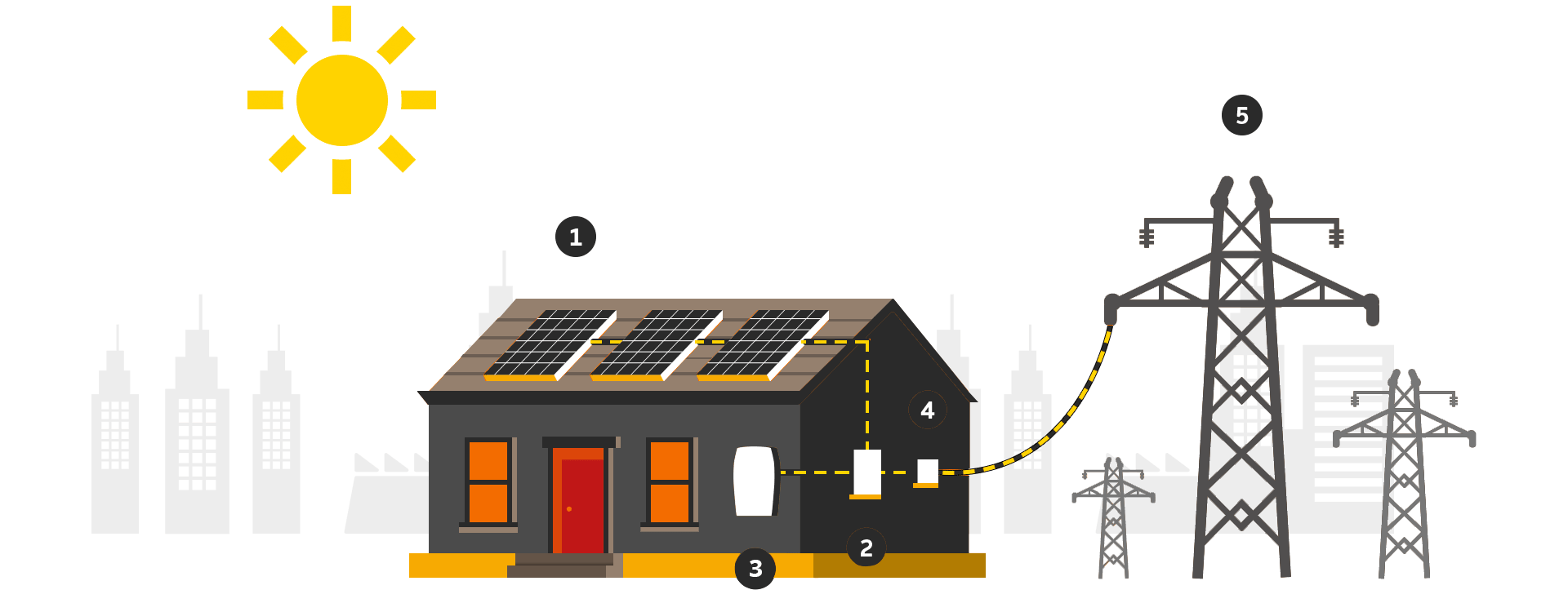
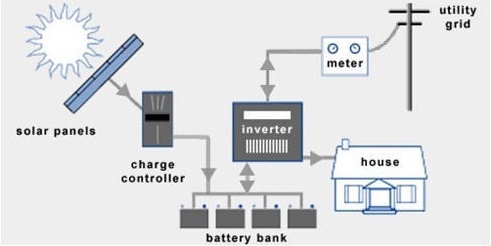
- When the photovoltaic panels are exposed to the sun’s rays, it absorbs the energy. This energy is transferred to negatively charged electrons They get attracted to a side of silicon cells enabling electric direct current (DC).
2. Inverter, a special electric equipment, converts the DC into Alternating Current (AC).
3. The AC is used to power households and the rest of the electric grid.
4. A Net Meter tracks all the incoming and outgoing electrical power. It shows the number of units fed to the grid and the units consumed. The user is only charged for the consumed units, gaining a concession on electricity bills.
5. A Grid is an electrical infrastructure that supplies the electricity. A grid is an important factor in designing the solar system. If solar power production is less than captive consumption, energy is instantaneously drawn from the grid.
Solar Energy History

Components of Solar System
Solar Panels
Silicon is used to make solar cells. These solar cells are put together, to form a solar PV Panel or Module. The solar panels convert sunlight into electricity.
They are positioned to face southward in a shadow-free area, mostly on the rooftops or ground. Solar panels vary based on their formation, performance, and material used.
Three types of these solar panels are:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are made from a single, purified silicon crystal, with a higher conversion efficiency (19-20%) of sunlight into electricity. Its complex manufacturing process makes it more expensive than other panels.
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Polycrystalline solar panels are made up of multiple silicon crystals, also called multi-crystalline solar panels. They are less expensive with a lower conversion efficiency (14-16%) and a simpler manufacturing process.
- Thin-film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are made using photovoltaic substances. These panels are lightweight, easy to install, and have lesser carbon footprints. However, they are less efficient and cheaper than other panels.
Inverter
A solar inverter is an important piece of equipment that converts DC, from the panels, into AC. Often considered the brain of the solar system, the inverter makes electricity safe for home usage.
It also provides analytical information that assists in fixing issues within the system.
The different types of inverters are:

String Inverters
A string inverter is the most cost-effective inverter that is highly common in residential areas for commercial purposes. It falls under an on-grid inverter and performs well in the non-shaded area.

Central Inverters
Central inverters are larger in size and handle up to 500KW per compound. They are usually used for huge commercial installations and utility-scale solar farms.

Microinverters
Micro inverters are suitable for residential and commercial purposes. They monitor the function of every single panel and transmit more energy in partially shaded locations.

Battery Inverters
Depending on the condition of the grid, battery inverters provide operation for critical loads. It converts the battery power into 230V AC and its usage is increasing by the day.

Hybrid inverters
Hybrid inverts are also known as multi-mode inverters that allow connecting batteries to the solar system. It has various features with a system that can be utilised without a battery backup.
Solar Panel Mounting Structures
The solar panel mounting structures support the solar panels at an angle facing the sun so they capture maximum solar radiation. These mounting structures should be designed in a weather-friendly manner so that it withstands floods or storms.
Solar Trackers
Solar trackers adjust in a way that the panels follow the movement of the sun. Single-axis trackers follow the movements of the sun from east to west during the day. Dual-axis trackers also follow the yearly north to south movements of the sun.
Although the trackers help in generating higher energy, it increases the total cost.
Bi-Directional Meter/Net Meter
The Bi-Directional Meter also called as “Net Meter” records how much electricity you send to and receive from the grid. As per the solar net metering policy in most of the states in INDIA, you will have to only pay for the difference in the electricity exported and imported every month.
Distribution Boxes
A distribution box (DB) protects by ensuring the flow of power in one direction. It has two types:
- Solar ACDB. It is installed between the solar inverter and home appliances and provides extra protection to the system. It contains a Surge Protection Device (SPD) that protects against power surges.
- Solar DCBD It is installed between the solar panels and the inverter. It contains a Surge Protection Device (SPD) that protects against high voltage and short circuits.
Grid
A grid is a collection of machinery and wires that supply all the generated energy. A grid is an important factor in designing the solar system. If an excess current is fed to the grid, it provides an optimal supply of necessary current for usage.
Grid
A grid is a collection of machinery and wires that supply all the generated energy. A grid is an important factor in designing the solar system. If an excess current is fed to the grid, it provides an optimal supply of necessary current for usage.
Grid Connected Systems or On-Grid Systems

Off-Grid Solar Systems

Hybrid System